Framework and Impact map
Individuals and communities
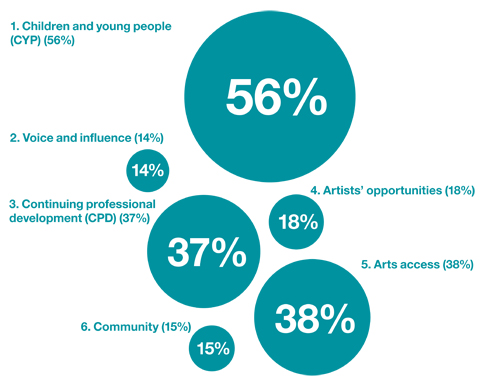
Percentage of Open Grants achieving each outcome. Most had several different outcomes; percentages do not add up to 100.
1. CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE (CYP)
Marginalised young people develop improved life skills and wellbeing and/or skills for a more successful future and enhance their employment prospects
- Develop attributes and skills that will facilitate the development of a more successful and happy future e.g. overall wellbeing, self-esteem, confidence, critical thinking, self-awareness, resilience, ability to build and manage relationships, team working, leadership
- Improve attendance at school or continue with HE courses, when at risk of drop-out
- Progress in their levels of attainment, gain qualifications or formal recognition of skills (accreditation)
- Move into jobs or volunteering or (re-) engage in education and training
- Improve speaking and listening skills
- Increase their engagement with learning, improve their behaviour for learning, and improve their capability for and attitude to lifelong learning
Young people who have been involved with the criminal justice scheme as offenders or suspects:
- Develop attributes and skills that will facilitate the development of a more successful, happy and stable future
- Reduce their incidence of re-offending
2. VOICE AND INFLUENCE
Actual and potential service users, particularly marginalised people, have increased voice in decisions about services that affect their lives
- Service users develop skills to make their views known and to have a dialogue with service providers
- Their views influence and shape decisions about service design and delivery
3. CONTINUING PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT (CPD)
Professionals/ practitioners/staff in a range of services and settings improve their practice and the results for the service users they work with, through participation in effective continuing professional development (CPD)
- General: Professionals/ practitioners/staff (apart from specialist groups below) gain new skills/ experience/learning, which equip them to improve their practice, for the benefit of service users
- Artists: Artists working in participatory settings have access to better quality CPD, the users/ participants they work with report greater satisfaction
- Teachers: Teachers and others in educational settings participate in CPD that improves their practice to the benefit of students’ learning
4. ARTISTS
Artists use new opportunities to pursue ideas and develop their work
- New opportunities used by artists to develop their work
5. ARTS ACCESS
People have increased access to and/or participate in arts/cultural activity
- New and larger audiences: Arts and cultural activities reach new and larger audiences
- New access: Groups with little or no experience of particular arts and cultural activities have new access (e.g. by visiting, viewing, listening)
- Arts participation: People participate in new arts/cultural experiences
- Longer term interest in the arts: People develop new, longer-term interest in the arts and an enhanced understanding of particular art forms or ideas
6. COMMUNITY
Communities are strengthened by the development of stronger relationships between people within the community
- Intergenerational relationships Intergenerational understanding and relationships are developed and sustained
- Relationships within or between communities
- Relationships are developed and/or strengthened within or between communities
Organisations
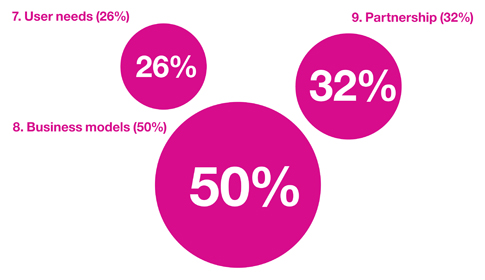
7. USER NEEDS
Organisations change their services in ways that demonstrably respond better to the needs of service users and local communities
- New groups: Organisations develop the capacity and capability to respond to groups new to them e.g. marginalised young people, and to develop appropriate new services or activities
- Galleries and museums community engagement: Community engagement becomes central to the ways in which museums and galleries work and results in collaborative
exhibition development - Mental health agencies and young people: Mental health agencies work with young people to develop services that provide earlier intervention and help young people
look after their own mental health more effectively
8. BUSINESS MODELS
Organisations develop new business models to enable new work or types of service and/or longer-term sustainability of the organisation and services, to the benefit of their service users
- New business models: New business models and forms of service delivery are developed, enhancing financial stability of the organisation and its services for users
- Leading to further funding: The success of PHF funded work enables organisations to make a successful case for continuing support/ funding from other funders or commissioners. Service users benefit from changes and the sustainability of services
- New evaluation practices: Organisations develop new models (in the form of tools, frameworks, methods or reporting) and/or skills by which they can more successfully
measure their outcomes or demonstrate their impact
9. PARTNERSHIP
Organisations develop new, formal collaborations, networks and partnerships. Partnership skills are sufficiently developed and embedded in the organisation to enable more effective services for/relationships with users in the future
- New and stronger partnerships and collaborations enable the improvement of services or creation of new ones, to the benefit of service users
Practice and policy
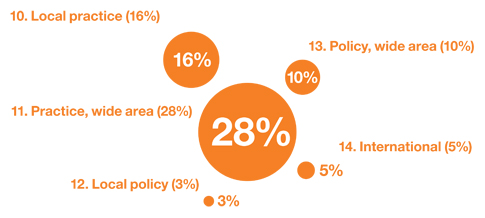
10. LOCAL PRACTICE
Significant numbers of organisations in the relevant sectors in the local area adopt practices, including innovations, shown through PHF-funded work and evaluation to improve outcomes for their service users/ target groups/ audiences etc.
- Local organisations adopt practices and ways of working that make them more responsive to users’ needs or community interest
- Local take-up of practices developed to encourage and sustain learning
- Local take-up of other practices
11. PRACTICE, WIDE AREA
Significant numbers of organisations in the relevant sectors, across a wide geographical area, adopt practices, including innovations, shown through PHF funded work and evaluation to improve outcomes for their service users/target groups/audiences etc.
- Users’ needs: Organisations across a wide area adopt practices/ways of working that make them more responsive to users’ needs or community interest
- Learning: Wide take-up of practices developed to encourage and sustain learning
- Student retention: Higher education institutions adopt practices found to be effective in increasing student retention
- General: Wide take-up of other practices
12. LOCAL POLICY
Politicians and policy makers at local levels develop awareness and understanding of
arguments for policy change, based on evidence from PHF funded work. In some cases, PHF evidence is known to influence a decision to change policy
- Influence on policy takes place at a local level
13. POLICY, WIDE AREA
Politicians and policy makers at national levels develop awareness and understanding of
arguments for policy change, based on evidence from PHF funded work. In some cases, PHF evidence is known to influence a decision to change policy
- Influence on policy takes place at a national level
14. INTERNATIONAL
Policy and/or practice internationally is influenced by the evidence of PHF funded work
- Influence on policy and/or practice takes place at an international level